The metal foam center of the Fraunhofer Institute for Machine Tools and Forming Technology IWU is your contact for the development of lightweight concepts and assemblies with metal foam. For that we offer a complete portfolio of products and services based from the idea development over the construction and simulation up to the assembly manufacturing and experimental quality analysis. We would also be pleased to advise you concerning alternative material concepts together with any other information you may require concerning the production material.
Metal Foam Center
Tabbed contents
What is metal foam?

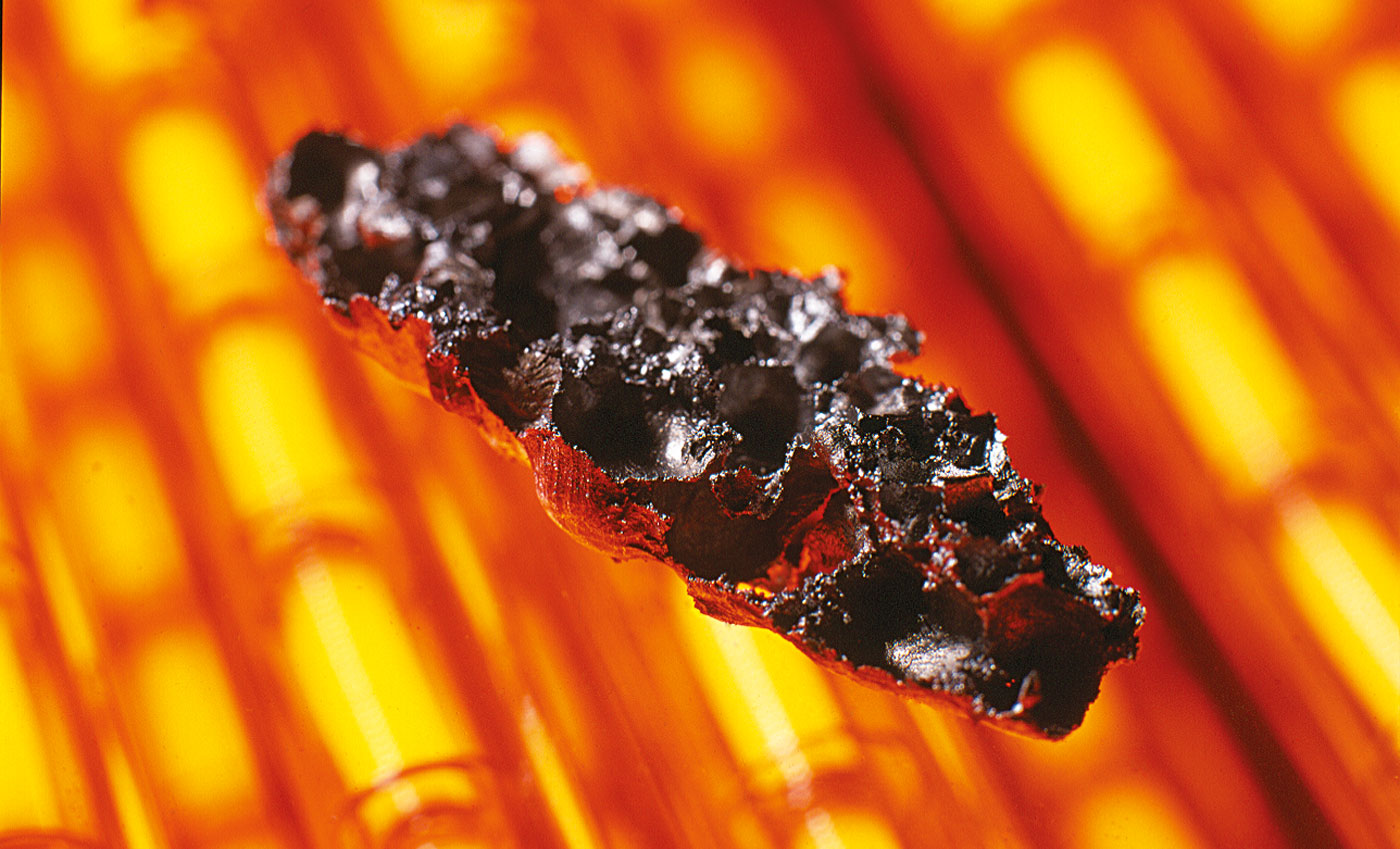
Metal foam is a high porous and very light material, equally to the model of Mother Nature, exemplified by wood and bones. Metal foams excellently absorb energy as vibration, impact and sound due to their cellular structure. Metal foams are, in general, significantly more stable and temperature resistant than plastic foams. Moreover, they are well suited for shielding electromagnetic waves.
The state of the art are foams based on aluminum and zinc which exhibit a density of less than 0.5 g/cm3, depending on the production method.
Metal foam is usually offered compositely with steel and aluminum sheets realized in sandwiches. Sandwiches feature a much higher bending stiffness than massive sheet metal plates with less overall weight. Due to their properties such as high stiffness and crash behavior, metal foams are highly applicable on many working fields.
At the end of their lifetime, metal foams und foam composites can be recycled without any problems.
Production
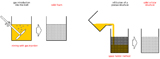
The production of metallic foams can be realized by using various processes. This refers to the distinction made between powder-metallurgical processes and metallurgic melting processes.
Powder-metallurgical process chain
The powder-metallurgical procedure route for foam production involves the mixing of a metal powder (e.g. aluminum) with a gas evolving propellant (e.g. titanium hydride). Further additives mostly serve as foam stabilizer. Subsequently the powder mixture gets compressed and gets foamed in a heat treatment process. The increase of volume for aluminum foams is five times higher than the initial volume – in accordance with that, foam densities of about 0.5 g/cm³ can be reached.
Range of services
Idea
When it comes to design capabilities and fields of application for metal foams, customers often have the best ideas. But perhaps we can inspire you with new solutions due to our day-to-day activities with this brand new working material.
Design / Simulation
We would be pleased to assist you with the design of your assembly. With the help of the Finite Element Method (FEM) we simulate the component behavior according to your wishes statically, dynamically and thermally so that weaknesses can already be recognized and eliminated in this early stage of development. The calculation of several alternatives and a relative comparison to the original construction is already taken into account. Properties can vary within certain limits and therefore can be adapted to the respective application by the modification of the foam density.
Construction
We design foamed parts and units according to your demands. These include conceptual, component and assembly drawings as well as part lists. The data can be transferred as Pro/ENGINEER®- or AutoCAD®-files. If the customer wants to start with a given design, we can offer you consultation on foam-friendly construction of the components. We are also prepared to give you our outmost support for questions on joining of the foam components together with other semi finished products of the assembly.
Production
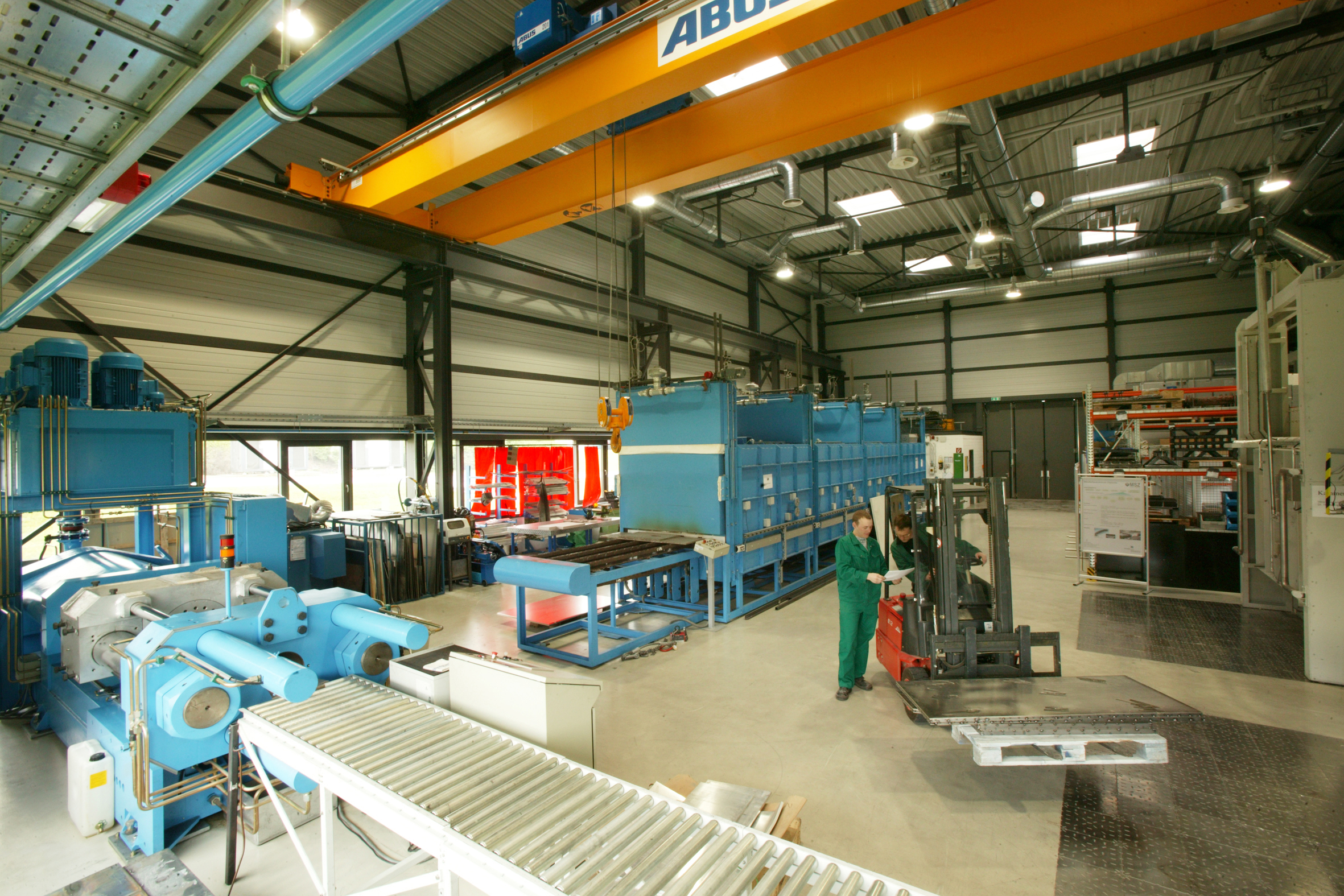
For the metal foam production we generally prefer aluminum foam and the powder metallurgical process. For the production several ovens are available in which discontinuous as well as continuous components can be foamed and heat treated. Components can be directly foam filled or foamed. Big assemblies are preferably built up from prefabricated foam semi-finished products such as sandwiches and foam filled profiles. Therefore the semi-finished products are foamed, tailored and generally joint together by welding according to the requirements.
Experimental property analysis
We offer you to test/analyze the produced assemblies individually or based on the installation condition. Therefore statically, dynamically and thermally measurements are possible.
As results we offer you statements on:
- Flexibility
- Deformation components
- Weak point analysis
- Harmonic response functions
- Natural frequencies
- Natural vibration forms
- Damping characteristics
- Operational vibration analysis
- Temperature distribution
- Acoustic performance
Is the aluminum foam not offering the desired effects?
In that case, we advise you with the selection of other materials and offer comparative material studies.
Fields of application
Sandwiches with aluminium foam core und massive cover sheets are excellently suited for lightweight constructions. The light aluminium foam core functions as a rigid core which holds the top layers at a distance. The top layers are responsible for the applied loads. Semi-finished products are significantly lighter than massive plates as the core material exhibits a low density while maintaining the same load carrying capacity.
This advantage in combination with good energy absorption capability predestines these semi-finished products for machine tool building – an acknowledged application represent machine slides.
Metal foam is also highly suitable as a wall and stiffening element in the building sector – extended with comfort functions such as heat storage and fire protection.
Metal foam can be used as a very good crash absorber in the automotive industry for example, owing to its cellular structure. Only after a high degree of deformation bearing structures of cars and commercial vehicles may be affected.
However, the application of the foam is not limited to this. The foam formation is associated with a high expansion. The material serves like an adhesive as the foam can bridge very big gaps and creates a metallurgical bonding with metals.
| Field of application |
Range of use |
|---|---|
| Automotive industry | Car body knots, longitudinal beams, crash absorber |
| Engineering | Fast moving vibrating devices |
| Building industry | Light floor- and wall elements with integrated comfort function, e.g. heat storage and fire protection |
| Shipbuilding industry | Hatches, doors, ribs, superstructures |
| Railway vehicles | Paving tiles, crash absorbers, complete front modules |
| Design | Partitions, adornments, decoration |
Products
We produce sandwiches, foam filled profiles and complex assemblies upon request and in agreement with our customers. Sandwiches with steel cover sheets can be foamed in a single piece with overall dimensions up to a maximum of 2,00 mm x 1,50 mm. Bigger dimensions can be realized with joining by welding. Foam core heights up to 50 mm can be reached, depending on the overall dimension.
If a heat treatment of the top layer is not possible or undesired, we also produce glued compounds. Compared to directly foamed components a greater evenness can be achieved.
Foam filled profiles can be produced with a length of no more than 6 m. Usually we produce foam out of aluminum alloys. We also offer foams of other base alloys upon request, e.g. zinc and copper.
Technical equipment
Indirect extrusion press
Continuous furnace
Infrared radiation oven
Chamber oven
(2 facilities)
Vacuum casting system with high-temperature furnace
- Tilt casting system with induction melting chamber and heatable casting mold
- Suitable for titanium alloys and stainless steel
- Maximum temperature crucibles: 1,750 °C
- Maximum temperature casting mould: 1,750 °C
- Melt volume approx. 5l
- Vacuum: 5 x 10-3 mbar
- Inert gases: argon, nitrogen
Publications
Selected recent publications
Handbook for Aluminium Foams; 1st edition; Aluminium publisher; 2007
Den Schwingungen einen Dämpfer versetzt! - Industrieanzeiger (2010) 29, S. 38-39
Hochdämpfende, zellulare Konstruktionswerkstoffe für den Werkzeugmaschinenbau - Metall 65 (2011) 1/2; S 32-36
Leichte Lösungen mit Zellularen Metallischen Werkstoffen - Ligthweightdesign (2010) 3, S. 60
Aluminiumschaum – Ein Werkstoff für das Bauwesen? Teil I: Herstellung, Eigenschaften, Bearbeitung und Anwendungspotential von Aluminiumschaum sowie Aluminiumschaum-Verbunden - Bauingenieur (2011) 3; S. 97-105
Aluminiumschaum – Ein Werkstoff für das Bauwesen? - Teil 2: Anwendungsmöglichkeiten für Aluminiumschaum sowie Aluminiumschaum-Verbunde - Bauingenieur (2011) 10; S. 425-432
Neue Leichtbaukonzepte aus Chemnitz - Binnenschifffahrt ZfB (2011) 4; S. 56-57
 Fraunhofer Institute for Machine Tools and Forming Technology
Fraunhofer Institute for Machine Tools and Forming Technology